Home-page - Icelandic Meteorological Office
Weather forecast
Weather forecast for the next 24 hours
Decreasing northwest- and westerly wind today. Intermittent snow or sleet in North-Iceland, but becoming mostly dry there in the afternoon. Dry weather elsewhere. Temperature around or above freezing.
Winds becoming stronger with precipitation in the evening and over night.
Northeast 10-18 m/s tomorrow, but 15-23 in the northwest part. Intermittent sleet or snow, but becoming dry in the southwest in the afternoon. Slowly moderating tomorrow evening.
Forecast made 14.03.2026 05:45
Forecaster's remarks
Snow or sleet in North-Iceland early on today, travellers are advised to check road conditions before setting off.
Increased wind with precipitation in the evening and over night. Blizzard in the northwest part tomorrow (Sunday), and difficult driving conditions near the south coast.
Prepared by the meteorologist on duty 14.03.2026 05:45
If the map and the text forecast differs, then the text forecast applies
Forecast for station - 1
Forecast for station - 2
Forecast for station - 3
Forecast for station - 4
Forecast for station - 5
Maximum wind in Iceland today
| Lowlands | |
|---|---|
| Highlands | |
|---|---|
Maximum and minimum temperature in Iceland today
| Lowlands | |
|---|---|
| Highlands | |
|---|---|
Maximum precipitation in Iceland today
| Lowlands | |
|---|---|
| Highlands | |
|---|---|
Maximum wind in Iceland during the last hour
| Lowlands | |
|---|---|
| Highlands | |
|---|---|
Maximum and minimum temperature in Iceland during the last hour
| Lowlands | |
|---|---|
| Highlands | |
|---|---|
Maximum precipitation in Iceland during the last hour
| Lowlands | |
|---|---|
| Highlands | |
|---|---|
Preliminary results
Earthquakes
Biggest earthquakes during the last 48 hours
| Size | Time | Quality | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.7 | 12 Mar 11:47:51 | Checked | 2.7 km W of Landmannalaugar |
| 2.7 | 14 Mar 06:58:45 | Checked | 8.8 km ESE of Bárðarbunga |
| 2.2 | 13 Mar 13:23:31 | Checked | 9.1 km WSW of Geirfugladrangur |
Specialist remark
On March 12th an earthquake M3.7 was detected around 3 km West of Landmannalaugar. The earthquake was at 1.3 km deep and was felt in the vicinity. Around 10 aftershocks have been detected, the largest M1.7.
This is the largest earthquake since January 2019 and August 2018 when earthquakes of M3.7 were also detected.
Written by a specialist at 13 Mar 19:43 GMT
Week overview -
Earthquake activity throughout the country is described in a weekly summary that is written by a Natural Hazard Specialist. The weekly summary is published on the web every Tuesday. It covers the activity of the previous week in all seismic areas and volcanic systems in the country. If earthquake swarms are ongoing or significant events such as larger earthquakes have occurred during the week, they are specifically discussed. More
Hydrology
Average flow and temperature last 24 hours
| River | Place | Flow | Water temperature |
|---|
Remarks of a specialist
Winter conditions are prevalent in many rivers, ice dams may form. There is an ice dam in Héraðsvötn and water has approached road 1, please proceed with caution.
Due to malfunction we have turned off the service publishing hydrological data on the map. Instead see the data using our Real-time monitoring system.
Written by a specialist at 12 Mar 15:57 GMT
Avalanche forecasts are now published on Icelandic Met Office’s new website:
New avalanche pages on gottvedur.is/en
News from the Icelandic Met Office’s landslide monitoring service will continue to be published on vedur.is (in Icelandic)
News
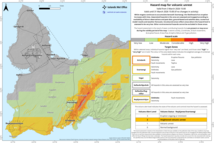
Magma accumulation beneath Svartsengi approaches 23 million cubic meters since the last eruption

Nordic report on the impacts of a AMOC tipping urges stronger mitigation, monitoring and preparedness
The report A Nordic Perspective on AMOC Tipping reviews the current state of science on the impacts of potential Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) collapse and provides recommendations for policy actions.
Read moreThe weather in Iceland in 2025
The year 2025 was the warmest year in Iceland since measurements began. The national average temperature was 5.2 °C, which is 1.1 °C above the average for the years 1991–2020 and the highest ever recorded. Temperatures were well above average for almost every month of the year. The spring weather was exceptionally favourable; it was the warmest spring ever recorded nationwide, and May was by far the warmest May on record. In mid-May, a 10-day heatwave occurred across the entire country. It was the most significant heatwave known in Iceland for the month of May. Overall, the weather in 2025 was unusually calm, with few stormy days and generally favourable conditions. It was relatively wet at the beginning of the year but dry toward the end. Snow cover was light across the entire country.
Read more
SeisComP becomes the new primary earthquake monitoring system of the Icelandic Meteorological Office
The implementation of SeisComP represents a major step forward in the development of the IMO's earthquake monitoring capabilities. Preparations have been underway for several years, and the system transition involves both technical and procedural changes aimed at improving analytical capability, data dissemination, and providing a more modern working environment for specialists.
Read more
The ninth eruption on the Sundhnúkur crater row has ended
Updated 5 August
The volcanic eruption that began on 16 July on the Sundhnúkur crater row is now officially over, and a new hazard map has been issued. Despite the end of the eruption, life-threatening conditions remain in the area due to unstable lava and the potential for gas pollution. Uplift has resumed, and magma continues to accumulate beneath Svartsengi.
Read moreHeavy thunder and lightning in Northwest Iceland and the Westfjords
By 11:00, more than 450 lightning strikes had been recorded since the activity began.
Read moreShort articles

Climatological data
Through links in this article, climatological information is available, i.e. monthly- and annual values of various weather components in Iceland since 1961. Averages provided are either monthly or annual averages. Temperature is given in degrees celsius, air pressure in hPa, humidity in percentages, precipitation in millimeters and windspeed in m/s.
Read moreNew publications and research
- Guðrún Nína Petersen (2025). Alviðruhamrar - Meteorological conditions
- Michelle Parks, Freysteinn Sigmundsson, Vincent Drouin, Ásta R. Hjartardóttir, Halldór Geirsson, Andrew Hooper, Kristín S. Vogfjörð, Benedikt G. Ófeigsson, Sigrún Hreinsdóttir, Esther H. Jensen, Páll Einarsson, Sara Barsotti & Hildur M. Friðriksdóttir. (2023).
- Sahar Rahpeyma, Benedikt Halldórsson, Birgir Hrafnkelsson & Atefe Darzi. (2023). Frequency-dependent site amplification functions for key geological units in Iceland from a Bayesian hierarchical model for earthquake strong-motions.
- Sara Klaasen, Solvi Thrastarson, Yesim Cubuk-Sabuncu, Kristín Jónsdóttir, Lars Gebraad, Patrick Paitz & Andreas Fichtner. Subclacial volvano monitoring with fiber-optic sensing: Grímsvötn, Iceland. (2023).
- Ismael Vera Rodriquez, Marius P. Isken, Torsten Dahm, Oliver D. Lamb, Sin-Mei Wu, Sigríður Kristjánsdóttir, Kristín Jónsdóttir, Pilar Sanchez-Pastor, John Clinton, Christopher Wollin, Alan F. Baird, Andreas Wuestefeld, Beat Booz, Eva P.S.Eibl, Sebastian Heimann, Bettina P. Goertz-Allmann, Philippe Jousset, Volker Qye, Vala Hjörleifsdóttir, Anne Obermann. (2002).
- Lamb, O.D., Gestrich, J.E., Barnie, T.D., Jónsdóttir, K., Ducrocq, C., Shore, M.J., Lees, J.M., Lee, S.J (2022). Acoustic observations of lava fountain activity during the 2021 Fagradalsfjall eruption, Iceland. Bull Volcanol 84, 96. doi.org/10.1007/s00445-022-01602-3
- Freysteinn Sigmundsson, Michelle Parks, Andrew Hooper, Halldór Geirsson, Kristín S. Vogfjörd, Vincent Drouin, Benedikt G. Ófeigsson, Sigrún Hreinsdóttir, Sigurlaug Hjaltadóttir, Kristín Jónsdóttir, Páll Einarsson, Sara Barsotti, Josef Horálek & Thorbjörg Ágústsdóttir (2022). Deformation and seismicity decline before the 2021 Fagradalsfjall eruption. Nature 609, 523–528. doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05083-4